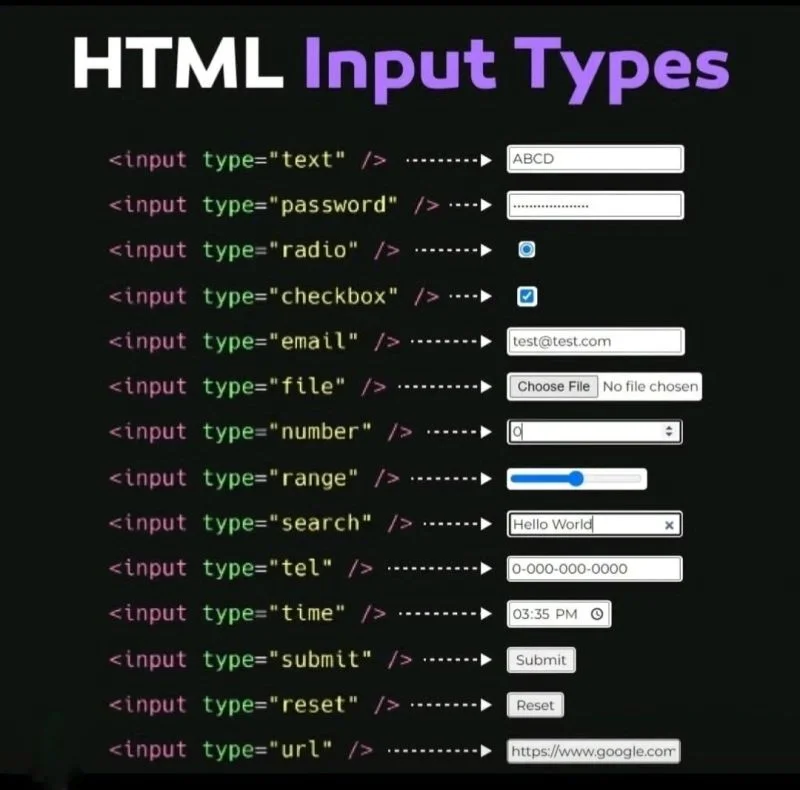
In modern web development, HTML forms play a crucial role in collecting user data. At the heart of these forms is the <input> element, which uses the input type attribute to define what kind of data a user can enter, ranging from text and numbers to dates, files, and more. Understanding the different input types is essential for building functional and user-friendly forms.
What are HTML input types?
HTML input types are values assigned to the type attribute of the <input> tag. They specify the expected format of user input and influence how browsers render the field. For instance, setting the input type to “email” prompts the browser to validate that a proper email address is entered, while using “file” enables file uploads directly through the form. There are over 20 standardized input types, each serving a unique purpose.
Importance of the input type attribute in forms
The input type attribute isn’t just for aesthetics or basic structure—it directly affects usability, accessibility, and data validation. By selecting the correct input type, developers can:
- Prevent invalid data entry (e.g., using type=”number” for numeric fields)
- Reduce reliance on JavaScript for basic validation
- Improve accessibility for screen readers and assistive technologies
- Tailor the interface to device-specific keyboards and behaviors (especially on mobile)
Overview of how input types enhance user experience
Using the appropriate input type improves the overall experience for users by making forms easier to fill out and reducing errors. For example, type=”date” provides a calendar picker, while type=”tel” triggers a numeric keypad on mobile devices. These subtle enhancements help users complete forms faster and more accurately. Ultimately, a well-chosen input type can increase form submission rates and improve user satisfaction.
Ready to become a full-stack software developer and build powerful web applications and end-to-end software solutions?
Join our comprehensive Software Engineering Course in Kenya! Our hands-on program is structured into focused modules covering front-end development, back-end development, APIs, and databases. Everything you need to launch a successful tech career.
Commonly Used HTML Input Types
Choosing the correct input type can dramatically improve form usability, validation, and data quality. Below are some of the most commonly used HTML input types, along with examples and best practices for implementation.
Text Input Type
The text input type is used for single-line text input.
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Enter your name">Usage:
This input type is ideal for names, titles, or short responses.
Attributes that enhance text input:
- placeholder: Provides hint text.
- maxlength: Limits the number of characters.
- required: Makes the field mandatory.
Password Input Type
The password input type masks the entered text with dots or asterisks.
<input type="password" name="user-password" required>Hiding sensitive information:
Used for login forms to protect user credentials.
Validation tips:
- Combine with pattern to enforce strength rules.
- Use JavaScript or browser APIs for real-time strength feedback.
Email Input Type
The email input type validates that the input resembles a valid email format.
<input type="email" name="user-email" placeholder="example@domain.com" required>Built-in validation features:
- Prevents form submission if input doesn’t match email pattern.
Best practices:
- Always pair with required.
- Use autocomplete=”email” for convenience.
Number Input Type
This input type is used to enter numeric values only.
<input type="number" name="quantity" min="1" max="10" step="1">Accepting numeric data only:
Useful for quantities, prices, or age.
Using min, max, and step:
- min and max set numeric limits.
- step controls allowed increments (e.g., 0.5 for decimals).
Date and Time Input Types
These input types provide UI elements like calendars or clocks.
<input type="date" name="birthday">
<input type="time" name="appointment-time">
<input type="datetime-local" name="event-start">Explanation:
- date: Calendar picker.
- time: Time selector.
- datetime-local: Date and time combined.
Browser support and fallbacks:
- Most modern browsers support these.
- For legacy browsers, consider a JavaScript date-picker library.
Checkbox and Radio Input Types
Used for selecting one or multiple options.
<!-- Checkbox -->
<input type="checkbox" name="interest" value="coding"> Coding
<!-- Radio -->
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male"> Male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female"> FemaleDifferences:
- checkbox allows multiple selections.
- radio allows only one selection within a named group.
Best practices:
- Always group radios by name.
- Provide clear labels for accessibility.
File Input Type
Used to allow users to upload files.
<input type="file" name="profile-picture" accept=".jpg,.png" required>Uploading files securely:
- Always validate file size and type on the server.
Accept attribute and restrictions:
- Use accept to limit file types (e.g., accept=”image/*”).
Range Input Type
Creates a slider for numeric input.
<input type="range" name="volume" min="0" max="100" step="10">Creating sliders:
Ideal for settings like brightness, volume, or satisfaction scores.
Enhancing interactivity:
- Pair with JavaScript to show current value in real time.
Color Input Type
Lets users pick a color from a palette.
<input type="color" name="favcolor" value="#ff0000">Use cases:
- Design or branding apps.
- Theme color customization forms.
Example:
A UI builder asking users to select a background color.
Best Practices for Using HTML Input Types
Choosing the right input type isn’t just about form functionality; it’s about creating a seamless, accessible, and mobile-friendly experience for your users. Below are best practices to guide you in using HTML input types effectively in modern web forms.
Matching the Correct Input Type to the Data Expected
One of the most important best practices is using the appropriate input type for the kind of data you expect users to submit. This not only improves data quality but also reduces user errors.
Examples:
- Use type=”email” instead of type=”text” for email addresses to enable built-in format validation.
- Use type=”number” for quantities or age to block non-numeric input.
- Use type=”date” for birthdates to provide a calendar interface.
Why it matters:
Using a precise input type communicates clear expectations to the browser, which in turn can provide built-in UI enhancements, validation, and feedback.
Improving Form Accessibility and Usability
Accessible forms ensure that all users including those using assistive technologies—can interact with your website effectively.
Tips:
- Always pair input types with <label> elements for screen reader compatibility.
- Use aria-* attributes for custom input interactions.
- Make sure keyboard navigation is seamless across all fields.
Example:
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>Clear labeling and proper use of the input type help users understand how to complete a form, improving both accessibility and form completion rates.
Just getting started with HTML and dream of becoming an expert web developer?
Enroll in our Web Development Course and learn to build responsive, scalable web applications from the ground up. Designed for beginners, this hands-on program can be completed in under 3 months, fast-tracking your journey into tech.
Responsive Design and Mobile Optimization with Appropriate Input Types
The right input type can improve the user experience on mobile devices by triggering the correct on-screen keyboard and input method.
Examples:
- type=”tel” brings up the number pad for phone input.
- type=”email” shows a keyboard with the “@” symbol for faster typing.
- type=”range” provides a touch-friendly slider for quick selections.
Mobile optimization matters because:
- A poorly optimized input type on mobile leads to user frustration and abandonment.
- Optimized input types increase form completion speed and accuracy.
Following these best practices when working with each HTML input type not only enhances the technical quality of your form but also ensures it’s user-centered, efficient, and accessible on all devices.
Choosing the Right HTML Input Type
The HTML input type attribute plays a vital role in shaping the functionality, usability, and overall success of any form. By specifying the correct input type, developers can ensure that user data is collected in the right format, validated efficiently, and submitted securely.
How the Input Type Impacts Form Functionality
Throughout this guide, we’ve seen how different input types from text, email, and password to file, range, and color, each serve a unique purpose. Choosing the proper input type determines:
- How the browser renders the input field
- What kind of data is accepted
- Which built-in validation and accessibility features are enabled
This directly influences how forms behave and how easily users can interact with them.
Importance of Using Specific Input Types for Better Data Handling
Using specific input types is not only a user experience decision it also streamlines backend processing. When a form field is clearly defined (e.g., type=”number”), you can confidently validate and store the data in a consistent format, reducing the chances of errors and security issues.
In short:
- Accurate input types lead to cleaner data
- They reduce the need for complex validation scripts
- They improve form reliability across browsers and devices
In conclusion, selecting the right HTML input type is essential for creating functional, user-friendly forms. It improves data accuracy, enhances usability, and simplifies validation. Each input type serves a specific purpose and should be used accordingly. By leveraging them effectively, you can greatly improve the user experience.