A clean and organized HTML structure is the foundation of any well-built website. Applying the best practices for HTML file organization not only improves readability and consistency but also ensures that your codebase is easy to maintain as your project grows. When files and folders are logically arranged, teams can collaborate more efficiently, developers can debug issues more quickly, and scaling the site becomes significantly easier. Whether you’re working solo or in a team, following structured HTML organization habits sets your project up for long-term success.
Beyond convenience, a well-organized HTML structure enhances professionalism and reflects attention to detail. Disorganized projects often lead to duplicated files, broken links, and lost productivity issues that grow more problematic as a website becomes more complex. On the other hand, a clean file structure supported by thoughtful naming conventions and modular code promotes clarity and enables seamless updates. Embracing the best practices for HTML file organization is a smart move that prepares your project for future development, team onboarding, and client handoffs, all while maintaining a consistent standard of quality.
Do you want to become a full-stack software developer and build real-world applications from the ground up?
Our hands-on Software Engineering Course in Kenya is built to launch you into a successful tech career. You’ll gain practical experience as you learn to design and develop complete software systems, mastering front-end and back-end technologies, APIs, databases, and more, all through project-based learning led by industry experts.
Importance of HTML File Organization:
Poor HTML file organization can lead to confusing code, broken links, longer development times, and an increased risk of errors. Disorganized files make it harder to find and update content, especially in larger projects. For example, a developer inheriting a messy project might spend hours locating the correct file or fixing mislinked resources time that could have been saved with a well-structured setup. Implementing the best practices for HTML file organization ensures a smoother workflow, minimizes mistakes, and makes maintaining or scaling your website much more manageable.
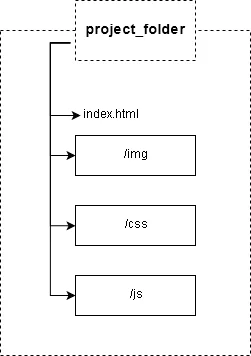
Folder and File Structure
A well-thought-out folder and file structure is a key part of the best practices for HTML file organization, helping developers navigate a project efficiently and reduce errors.
A. Root Directory Setup
Your root directory should contain only essential files, typically starting with index.html as the homepage. Stick to standard naming conventions such as lowercase letters, hyphens instead of spaces, and clear, descriptive names (e.g., about.html, not AboutPageFINAL.html). Keeping the root clean and minimal makes the project easier to understand at a glance.
B. Subfolders
Organize supporting files into clearly labeled folders:
- /css for stylesheets
- /js for JavaScript files
- /images for all image assets
- /fonts for custom fonts
- /media for videos or other media files
This separation helps prevent clutter and allows quick access to specific resources.
C. Keeping It Modular
For larger projects, break your HTML into partials like header.html, footer.html, and nav.html using templating engines or frameworks that support includes. This modular approach not only keeps individual files shorter and more manageable but also improves reusability and makes updates easier change it once, and it updates everywhere. It’s a powerful method within the best practices for HTML file organization that contributes to clean, scalable code.
Naming Conventions
Following consistent and clear naming conventions is a fundamental part of the best practices for HTML file organization. It enhances clarity, reduces confusion, and makes collaboration smoother.
A. File and Folder Names
Use lowercase letters, hyphens instead of spaces or underscores, and descriptive terms that accurately reflect the file’s purpose. For example:
- Good: about-us.html, main-style.css, user-profile.js
- Avoid: AboutUs.HTML, MainStyle.CSS, userProfile.js
This approach ensures files are easily readable across different systems (some of which are case-sensitive) and makes locating files more intuitive.
B. Consistency Across the Project
Maintaining consistent naming throughout your project avoids unnecessary confusion. If some files use camelCase while others use hyphen-case, or if some folders are plural and others are singular, it can slow down development and lead to mistakes. A unified naming convention, applied from the start, supports the overall structure and maintainability of your project an essential outcome of proper HTML file organization.
Commenting and Readability
Readable code is just as important as functional code. As part of the best practices for HTML file organization, using clear comments and consistent formatting helps you and your team understand and maintain the codebase efficiently.
A. Commenting Sections
Use HTML comments (<!– comment –>) to label and separate major sections of your page, such as headers, footers, navigation, or main content. For example:
<!-- Navigation Bar -->
<nav>...</nav>
<!-- Main Content -->
<main>...</main>These comments make scanning through long HTML files easier and guide anyone unfamiliar with the structure to the right section quickly.
B. Indentation and Line Spacing
Consistent indentation (usually 2 or 4 spaces per level) and logical line spacing greatly improve code readability. Proper formatting makes nested elements easier to follow and helps spot missing or misplaced tags. It also reduces the likelihood of syntax errors, which is especially helpful when collaborating with others or revisiting your own code later.
Clean, well-commented, and neatly indented HTML reflects professionalism and aligns perfectly with the best practices for HTML file organization.
Version Control and Documentation
Another essential part of the best practices for HTML file organization involves using version control and proper documentation. These practices not only help track changes but also make onboarding and collaboration easier.
A. Git Integration
Integrating Git into your workflow allows you to track every change made to your HTML and related files. It’s especially useful when working in teams, as it helps manage contributions, resolve conflicts, and maintain a history of the project. Version control tools like GitHub or GitLab also make it easy to roll back to previous states if something goes wrong, adding a layer of safety and accountability to your development process.
B. README Files
A well-written README.md file at the root of your project serves as a quick guide for anyone working with the code. It should include:
- A brief project description
- Instructions on how to run or build the project
- An overview of the folder and file structure
- Any dependencies or special setup requirements
By documenting this information clearly, you provide future collaborators or even your future self with the context needed to work efficiently, supporting long-term maintainability in line with the best practices for HTML file organization.
Tools and Best Practices to Enforce Structure
Even with the best intentions, maintaining a consistent and clean codebase can be challenging without the right tools. As part of the best practices for HTML file organization, using linters, formatters, and validators helps enforce structure and uphold quality.
A. Linters and Formatters
Linters are tools that analyze your HTML for syntax errors, bad practices, and inconsistent formatting. Formatters go a step further by automatically fixing these issues ensuring your code remains clean and uniform. Tools like Prettier and HTMLHint can be integrated into your code editor or build process to format files on save, saving time and maintaining a professional standard across the project.
B. HTML Validators
HTML validators, like the W3C Markup Validation Service, check your code against official HTML specifications. They help catch common mistakes such as unclosed tags, deprecated elements, or improper nesting. Regular validation ensures your site is accessible, functional across browsers, and built on a solid foundation key goals of any HTML file organization strategy.
Incorporating these tools into your workflow not only enforces discipline but also aligns your project with modern development standards and the best practices for HTML file organization.
To conclude, implementing the best practices for HTML file organization is more than just a matter of cleanliness; it’s a strategic approach to building efficient, scalable, and maintainable web projects. From establishing a logical folder structure and using consistent naming conventions to writing readable code and leveraging tools like linters and version control, these practices set the foundation for professional and collaborative development.
By adopting these methods, you’ll find that your workflow becomes smoother, teamwork more effective, and future updates less stressful. Whether you’re managing a simple website or a large-scale application, good organization pays off in the long run.
Just getting started with HTML and ready to dive into web development?
Our beginner-friendly Web Development Course takes you from the fundamentals to building responsive, scalable websites and dynamic web applications from the ground up. In less than 3 months, you’ll gain hands-on experience, learn in-demand tools and technologies, and build real-world projects—with expert guidance every step of the way.
Take time to evaluate your current HTML file organization. Refactor where needed, and start applying these best practices moving forward, you’ll thank yourself later.