CSS stands for Cascading Style sheets. It is a stylesheet language used to describe the presentation of a document written in HTML or XML.
It controls the layout, design, colours, fonts, spacing, and overall appearance of web pages. CSS allows developers to separate the content structure (HTML) from the visual design, making websites more flexible and easier to maintain.
By defining styles in an external file, CSS ensures that the design can be applied consistently across multiple web pages with minimal effort.
To begin your journey as a software developer? Enroll in our software engineering course in Kenya. We offer hands-on practical skills that make you a software developer in less than 10 months.
What is CSS in Web Development
CSS is crucial in web development by making websites visually appealing and user-friendly. Without CSS, web pages would display plain, unstyled text and elements, making the browsing experience less engaging. CSS allows developers to:
- Create visually attractive layouts: Using techniques like grids, flexbox, and responsive design, CSS enables web developers to build structured, eye-catching web pages.
- Improve user experience: Through interactive features like hover effects, transitions, and animations, CSS makes websites dynamic and interactive.
- Ensure responsiveness: CSS enables websites to adjust to different screen sizes, from mobile devices to large desktop monitors, ensuring a seamless user experience across devices.
- Enhance performance: CSS reduces the need for repetitive styling within HTML, which helps improve loading times and website performance
Structure of CSS: Selectors, Properties, and Values
CSS follows a simple structure comprising selectors, properties, and values, which define how HTML elements should be styled.
1. Selectors
A selector is used to target HTML elements that you want to style. It defines which elements on the webpage the CSS rule should apply to. For a clear academic explanation of selector concepts including type, class, ID, and combinators see the Stanford CS 106E lecture notes on CSS structure and selectors.
Types of CSS Selectors:
Element Selector: Targets all elements of a specific type (e.g., p for paragraphs, h1 for headings).
Class Selector: Targets elements with a specific class attribute, denoted by a dot (.) before the class name (e.g., .button for elements with the button class).
ID Selector: Targets an element with a specific id attribute, denoted by a hash (#) before the ID name (e.g., #header for the component with the header ID).
Universal Selector: Targets all elements on the page, denoted by an asterisk (*).
Attribute Selector: Targets elements with a specific attribute (e.g., [type=”text”] targets all input elements of type text).
Pseudo-classes: Targets elements based on their state (e.g., :hover for an element when hovered over).
Pseudo-elements: Targets specific parts of an element (e.g., ::before or ::after).
2. CSS Properties
A property is a characteristic of an element you want to change or style. Properties define aspects like colour, font, size, position, and more. To learn more about CSS properties, check out this complete guide to CSS properties.
Examples of common properties:
- color: Defines the text color of an element.
- background-color: Sets the background color of an element.
- font-family: Specifies the font for the text.
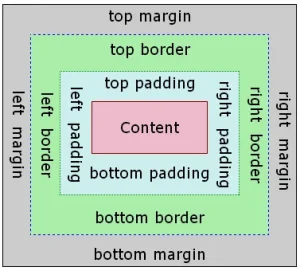
- margin: Controls the space outside the element.
padding: Controls the space inside the element. - border: Defines the borders around an element.
- width and height: Set the size of an element.
3. Values
A value is assigned to a property to define how it should be styled. Values can be specific measurements, colors, keywords, or functions. Examples of values:
- Color values: red, #ff0000, rgb(255, 0, 0), rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.5)
Length values: px (pixels), em, rem, %, vw, vh - Keywords: block, inline, none, auto
Numeric values: 1, 50, 0.5
Example of CSS Syntax:
selector {
property: value;
selector {
property: value;
}Example:
h1 {
color: blue;
font-size: 32px;
text-align: center;
}In this example:
- h1 is the selector (targeting all <h1> elements).
- color, font-size, and text-align are the properties.
- blue, 32px, and center are the values for the respective properties.
This structure allows you to create detailed styles for different elements on a webpage.Ready to go beyond the basics and start building real websites? Join our web development course and learn how to style, structure, and launch professional web projects from the ground up.
CSS Inheritance and Specificity
CSS Inheritance
Inheritance is a fundamental concept in CSS that allows certain properties to be passed down from parent elements to their child elements automatically. This means that if a style is applied to a parent element, certain child elements will inherit those styles unless otherwise specified.
Inherited Properties: Some properties are inherited by default, such as color, font-family, font-size, line-height, and text-align. For example, if you set the text color on the <body> element, all text inside the body will inherit that color unless another color is applied directly to a specific element.
Example
body {
color: blue; /* All text within the body will inherit this color */
}Non-Inherited Properties: Most layout properties like margin, padding, border, background, and width do not inherit by default. These properties must be explicitly defined for each element.
div {
margin: 20px; /* This will not be inherited by child elements */
}To prevent inheritance, you can set inherit, initial, or unset on properties:
- inherit: Forces inheritance of a property even if it is not inherited by default.
- initial: Resets a property to its default value.
- unset: Resets a property to either its inherited value (if applicable) or the default value.
CSS Specificity
Specificity is the process by which browsers determine which CSS rule takes precedence when multiple rules target the same element. The more specific a CSS selector is, the higher its priority over other less specific selectors.
CSS specificity is calculated based on a set of rules that determine the weight of a selector:
- Inline styles: Styles written directly on an HTML element (e.g., <div style=”color: blue;”>) have the highest specificity.
- IDs: Selectors targeting an element by id (e.g., #header) are more specific than class, attribute, and element selectors.
- Classes, attributes, and pseudo-classes: Selectors like .btn, [type=”text”], or :hover are less specific than ID selectors but more specific than element selectors.
- Element selectors: Selectors targeting an element type (e.g., h1, p, div) have the lowest specificity.
The specificity of a selector is calculated using a four-part value: (a, b, c, d), where:
- a = Number of inline styles
- b = Number of IDs in the selector
- c = Number of classes, attributes, and pseudo-classes
- d = Number of element selectors and pseudo-elements
Specificity Calculation Example:
For the following selectors:
- div (specificity: 0, 0, 0, 1)
- .container (specificity: 0, 0, 1, 0)
- #main (specificity: 0, 1, 0, 0)
- div.container (specificity: 0, 0, 1, 1)
In case of conflicting styles, the rule with the highest specificity wins. So if both .container and div.container set the same property, div.container will take precedence because it has a higher specificity (due to the combined element and class selectors).
Basic CSS Syntax
CSS follows a simple and structured syntax that consists of selectors, properties, and values. Here’s a breakdown of the syntax:
selector {
property: value;
}- Selector: Specifies which HTML element(s) to style.
- Property: Defines the aspect of the element to be styled (e.g., color, font size, etc.).
- Value: Specifies the setting or value for the property (e.g., blue, 16px).
1. Element Selector
Targets HTML elements by their name. For example, h1, p, or div.
Example:
h1 {
color: blue;
}This styles all <h1> elements by changing their text color to blue.
2. Class Selector
Targets HTML elements with a specific class attribute. It is denoted by a dot (.) before the class name.
Example:
.btn {
background-color: green;
color: white;
}This styles all elements with the btn class, setting the background color to green and the text color to white.
3. ID Selector:
Targets an HTML element with a specific id attribute. It is denoted by a hash (#) before the ID name.
Example:
#header {
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: bold;
}This styles the element with the id=”header”, making the font size 24px and font weight bold.
4. Universal Selector:
Targets all elements on the page, denoted by an asterisk (*).
Example:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}This removes any default margin and padding from all elements.
5. Descendant Selector:
Targets elements that are descendants of a specified element.
Example:
div p {
color: red;
}This targets all <p> elements that are inside a <div> element and sets their text color to red.
Properties and Values in CSS
Properties define the visual characteristics of the targeted elements, and values specify the settings for these properties.
1. Color Property
The color property is used to set the color of text.
Example:
p {
color: blue;
}2. Font-size Property
The font-size property controls the size of the text.
Example:
h1 {
font-size: 32px;
}3. Padding Property
The padding property controls the space inside an element, between the content and the border.
Example:
div {
padding: 20px;
}This adds 20px of space inside the div element.
4. Margin Property
The margin property controls the space outside an element, between the element and other elements.
Example:
.box {
margin: 10px;
}This adds 10px of space around the box element.
5. Background-color Property
The background-color property sets the background color of an element.
Example:
div {
background-color: lightgray;
}6. Text-align Property
The text-align property controls the horizontal alignment of text inside an element.
Example:
p {
text-align: center;
}This centers the text inside the p element.
7. Width and Height Properties:
The width and height properties define the size of an element.
Example:
.container {
width: 80%;
height: 400px;
}Examples of Basic CSS Code Snippets
Here are a few examples of how you can use CSS selectors, properties, and values together:
Styling a Header (h1) Element:
h1 {
color: darkblue;
font-size: 36px;
text-align: center;
margin-top: 20px;
}This will set the text color of all <h1> elements to dark blue, with a font size of 36px, center-align the text, and add 20px of space above the header.
Styling a Button Class:
.btn {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
padding: 15px 32px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
}This will style all elements with the class .btn to have a green background, white text, 15px vertical and 32px horizontal padding, and rounded corners.
Styling a Specific ID (e.g., #main):
#main {
background-color: #f4f4f4;
padding: 20px;
width: 100%;
}This will apply a light gray background, 20px padding, and set the width of the #main element to 100% of its container.
Responsive Styling Using Media Query:
@media screen and (max-width: 600px) {
body {
font-size: 14px;
}
.container {
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
}
}This media query changes the font size to 14px and makes the .container element take up 100% of the width when the screen width is 600px or less (mobile devices).
Summary:
- Selectors target elements on a webpage.
- Properties define the styling characteristics (e.g., color, font-size, padding).
- Values specify how the properties should be applied (e.g., color names, pixel values, percentages).
These building blocks allow you to create visually appealing and well-structured web pages.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a powerful tool that plays a vital role in web development by controlling the visual presentation of HTML content. It allows developers to design modern, responsive, and visually appealing websites by customizing layout, colors, fonts, and overall aesthetics. Understanding how CSS works and how to use it effectively is essential for creating engaging user experiences and building professional-quality websites. As you continue your journey in web development, mastering CSS will empower you to bring your creative ideas to life on the web.